The World’s Most Advanced End-to-End In Silico Platform for Rigorous Science-Backed Drug Development








Operating at the Intersection of Scientific Innovation and Regulatory Standards
Scientific innovation
Access to cutting-edge, validated research, and technologies through a broad global network of partners
Regulatory standards
FDA, EMA and industry, compliance + contributors to the development of emerging good practice frameworks
Including ‘Toward Good Simulation Practice’
(Co-authored with the U.S. FDA)
Make earlier, safer decisions with less time, cost, and risk
Decreased reliance on in vivo studies and early human exposure, consistent with FDA initiatives encouraging alternatives to traditional animal testing.

Time and Cost Saving







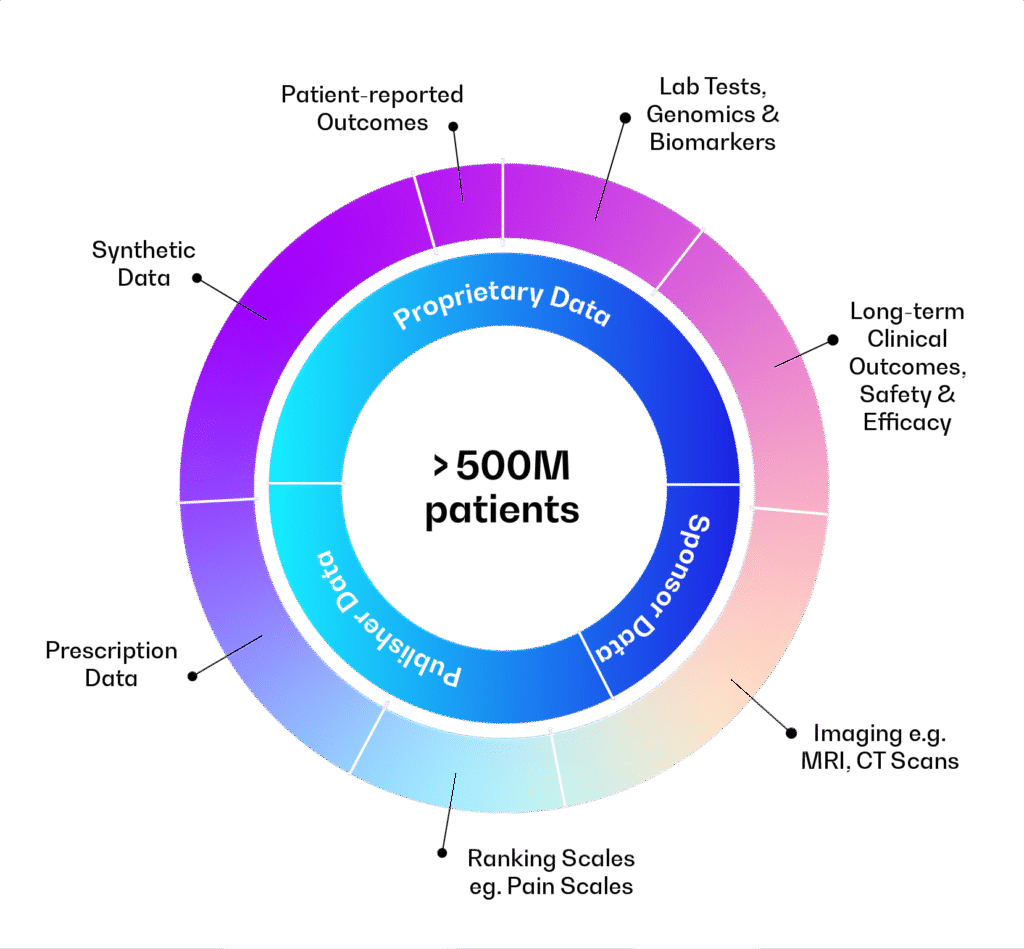
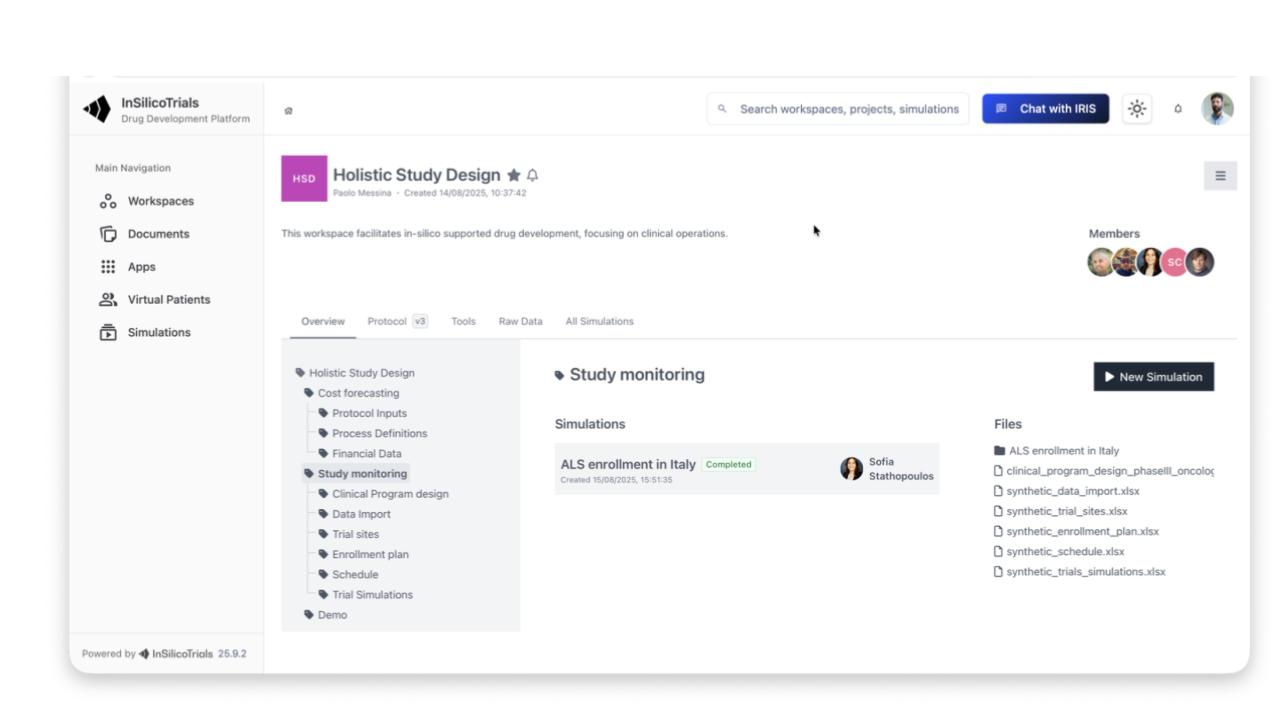
A Unified Data Integration Framework Powering Multi-Modal Data at Global Scale

Continuous optimisation loop
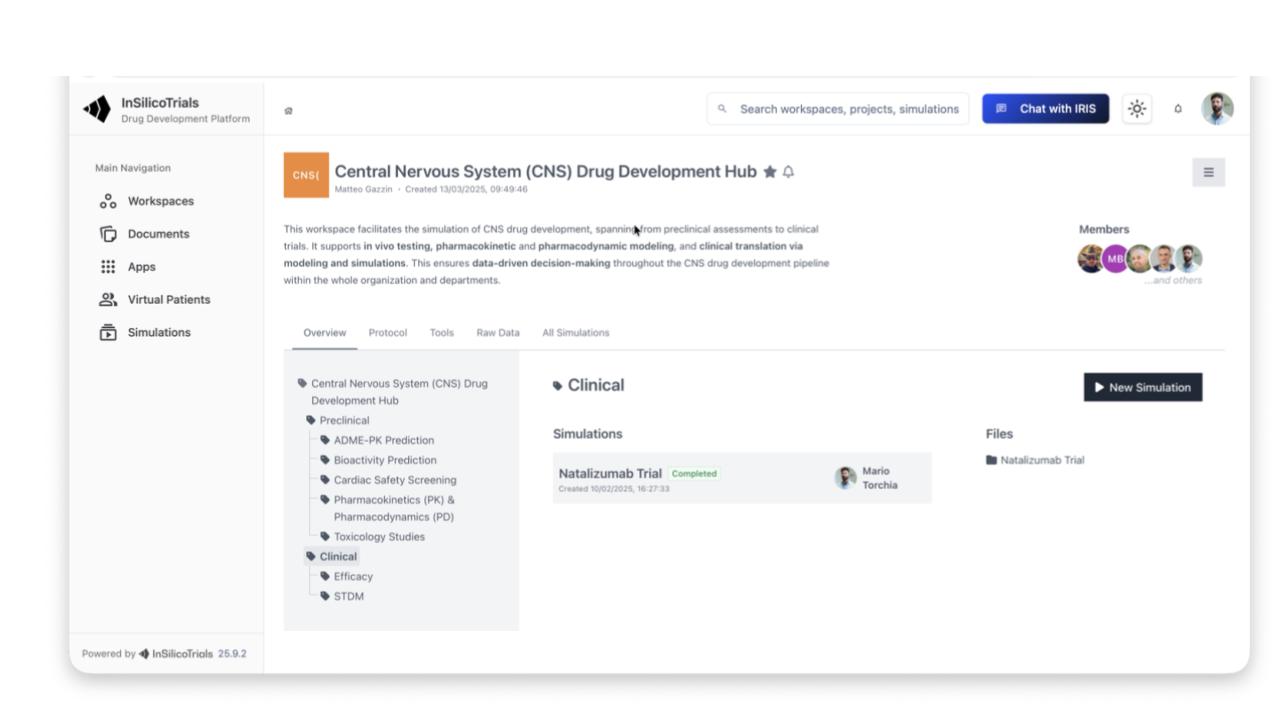
Enables clinical trial simulation, including synthetic patient generation and scenario comparisons: dosing, sample size, I/E criteria, adaptive designs, statistical methods
Includes Model Library, Data Library, data Integrator, Workflow Builder, Clinical Trial Simulator, Output Dashboard
Supports safety, efficacy, biomarkers, disease progression, QSP, multi-omics, in vitro/in vivo, and AI/ML models
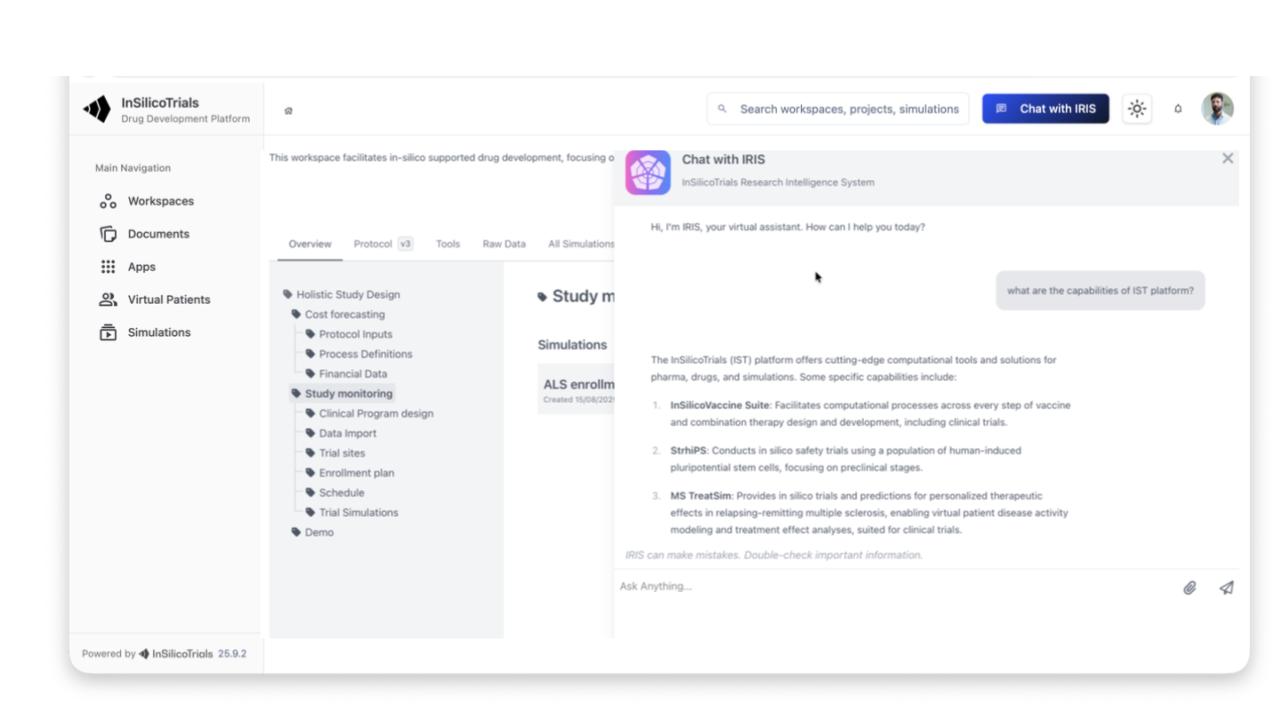
AI support for external information seeking through a multi-agent archite cture that connects tools, internal information, external information, and the simulation platform
Searches external sources (e.g., clinicaltrials.gov) to suggest clinical trial designs
Interprets data, makes recommendations, and analyses simulation results
Independently launches new simulations based on retrieved information and user preferences
Enables clinical trial simulation, including synthetic patient generation and scenario comparisons: dosing, sample size, I/E criteria, adaptive designs, statistical methods
Includes Model Library, Data Library, data Integrator, Workflow Builder, Clinical Trial Simulator, Output Dashboard
Supports safety, efficacy, biomarkers, disease progression, QSP, multi-omics, in vitro/in vivo, and AI/ML models
Awards
ARPA-H CATALYST - CARDIOVERSE digital-twin program
FDA’s GenAI Precision Challenge Top 5 Winner
London AI Summit Winner
Grind AI Startup of the Year Winner
Flagship Cases
Challenge
A development team needed to optimise a monoclonal antibody’s design and dosing before entering animal
studies, reducing wet-lab iteration cycles and early development risk.

Therapeutic Area:
Monoclonal antibody programmes. Preclinical.

Tech:
Mechanistic PK/PD and TMDD modelling, AI-assisted simulation, virtual patients
Savings:
12 – 30 months and $15 – 30M
Approach
AI-assisted Target-Mediated Drug Disposition (TMDD) modelling
Simulation of clearance, affinity, and dosing frequency scenarios
Virtual patient simulations to predict exposure and target engagement.
Result
Identified an optimised antibody variant with improved affinity, reduced clearance, and
stronger target suppression through in-silico experimentation.
Value
Accelerated preclinical optimisation
Reduced reliance on in vivo studies
Increased confidence before first-in-human studies.
Challenge
Ultra-small patient populations made traditional ALS trial designs underpowered, slow,
and ethically challenging.

Therapeutic Area:
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Phase II.

Tech:
ML disease-progression models, synthetic control arms, causal inference
Savings:
1 – 2 years and $10 – 40M
Approach
AML-based modelling of ALS disease progression
Generation of synthetic control patients
Causal inference to enable unbiased treatment comparisons.
Result
Augmented the control arm with 60 synthetic patients, increasing statistical power
while reducing the number of patients assigned to placebo.
Value
Improved trial feasibility in rare disease settings
Reduced patient burden
Faster, more confident go/no-go decisions.
Challenge
A large pharma organisation needed to optimise the dosing strategy for an antibody – drug conjugate,
balancing exposure, tumor control, and thrombocytopenia risk.

Therapeutic Area:
Oncology (ADC). Phase III design.

Tech:
QSP digital twins, PK/PD, tumour growth and safety modelling, PoS simulation
Savings:
6 – 18 months and $2 – 50M
Approach
Multi-scale digital twins linking PK, tumor dynamics, and platelet counts
ML and causal comparisons of fixed vs. adaptive dosing
Probability of Success (PoS) modeling across virtual populations.
Result
Revealed the optimal weekly regimen with superior efficacy and acceptable safety
trade-offs, guiding Phase 3 strategy.
Value
AI-augmented decision-making for pivotal trials
Higher PoS and smarter resource allocation
Quantified benefit–risk trade-offs before investing in large trials.
Challenge
A pharma team needed to evaluate long-term dosing strategies and safety outcomes without conducting
multi-year clinical trials.

Therapeutic Area:
Multiple Sclerosis. Label extension phase.

Tech:
QSP immune-system modelling, long-term (5-year) clinical trial simulation
Savings:
3 – 5 years and $50 – 150M
Approach
QSP modelling of immune response and lymphocyte dynamics
Simulation of relapse rates across virtual MS populations
Long-horizon (5-year) treatment strategy evaluation.
Result
Identified an optimised antibody variant with improved affinity, reduced clearance, and
stronger target suppression through in-silico experimentation.
Value
Evidence to support label extension without new long-term trials
Reduced development time and cost
Improved understanding of long-term benefit–risk profiles.
